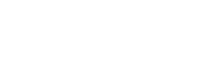About Us
Epilytics a epidemiology consulting group that specializes in all areas of epidemiology and data analysis with a focus on questions on Causal Inference. We specialize in assessing a wide range of services from reviewing grants and manuscripts to undertaking complex data analysis using Big Data.
We are a team of scientists which includes epidemiologists, biostatisticians, statistical modellers and data analysists with extensive experience in tackling the most complex epidemiological questions. The group is led by Mahyar Etminan an epidemiologist and clinical pharmacologist with over 200 publications in high ranked including JAMA, BMJ, Lancet, American Journal of Epidemiology, International Journal of Epidemiology.
We have extensive experience in both clinical and methods-based studies or porjects. In addition to publishing in high ranked journals, our studies have been used by drug regulatory agencies including the FDA, European Medicines Agency and Health Canada and covered by prestigious mainstream media including the ones listed below.
Nature
The Wall Street Journal
JAMA
BMJ
CNN
New York Times
Science
The Lancet
What we do
Case-control Studies
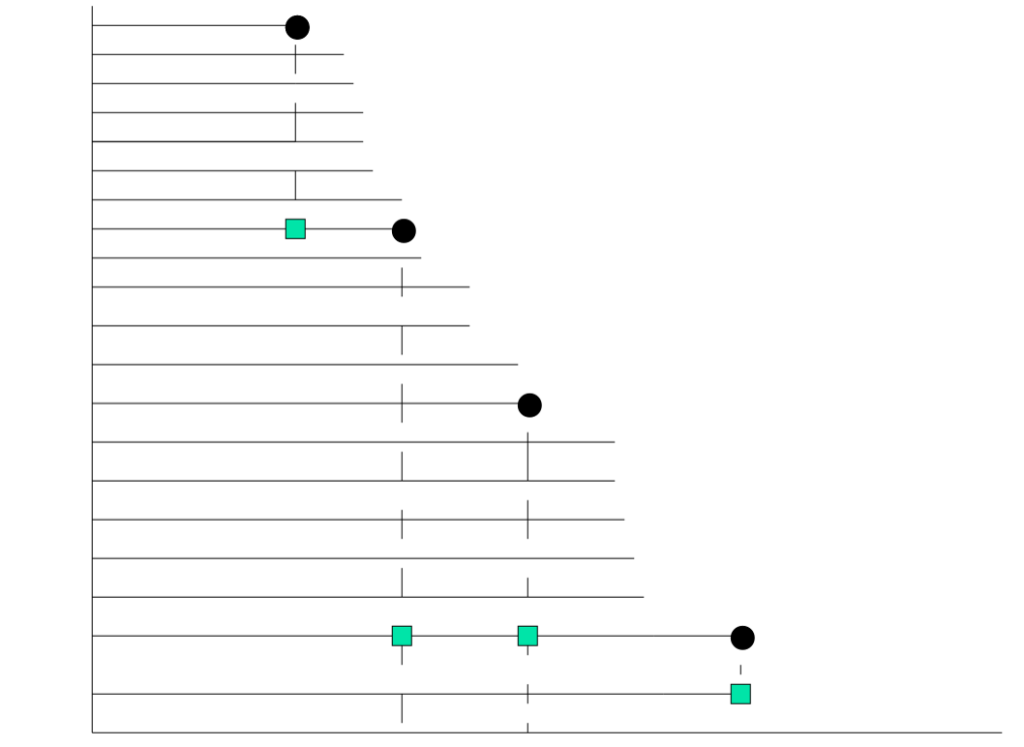
Cohort Studies
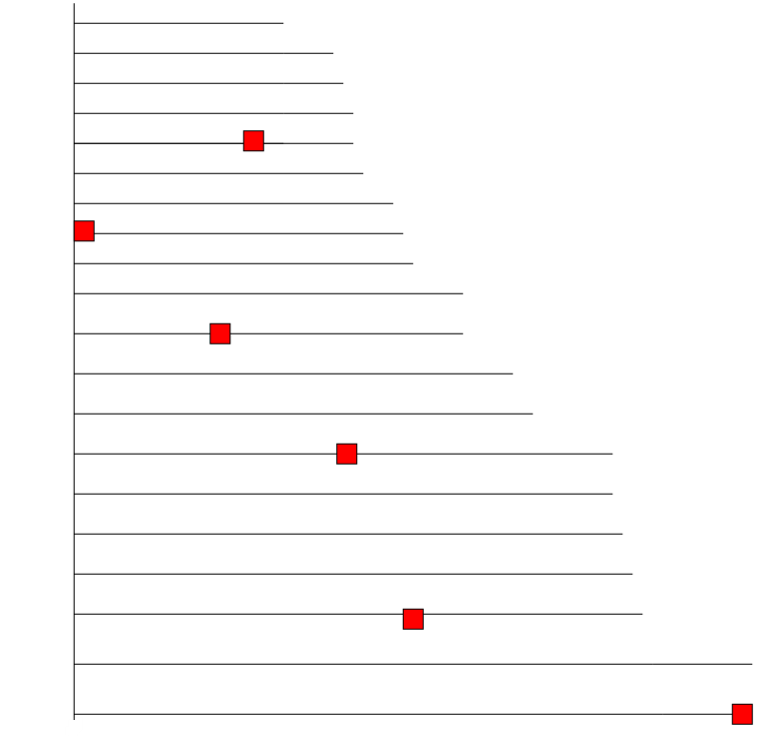
Causal Inference
Meta-Analysis
Propensity Score Matching
Publications
Publications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease:
Etminan M, Forooghian F, Brophy JM, Bird S, Maberley D. (2012).